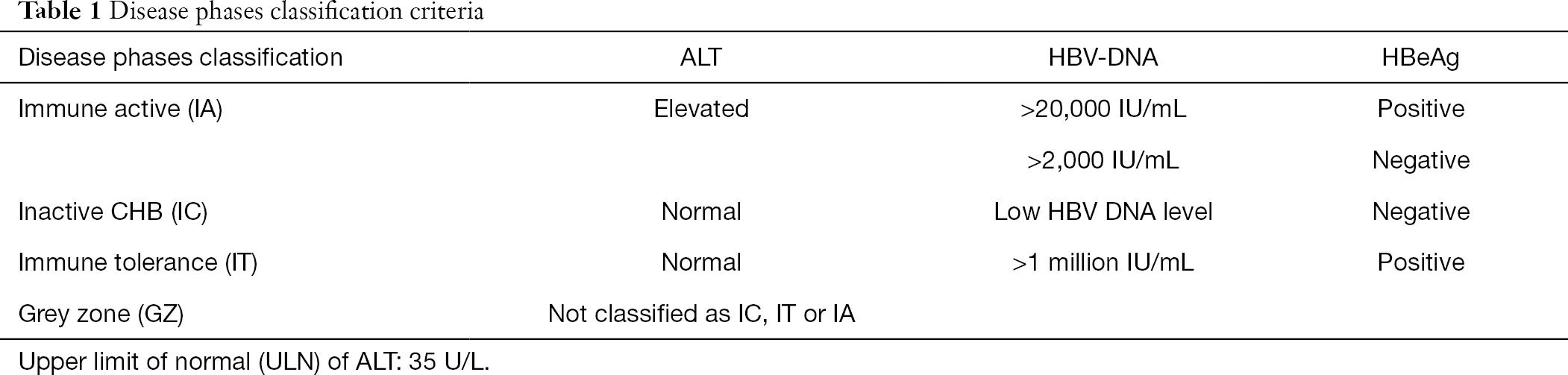
Hbv Dna Iuml
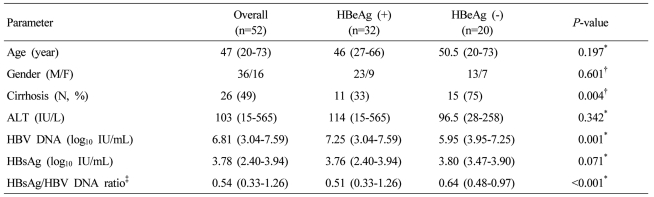
Pretreatment Serum Hbsag To Hbv Dna Ratio Predicts A Virologic Response To Entecavir In Chronic Hepatitis B
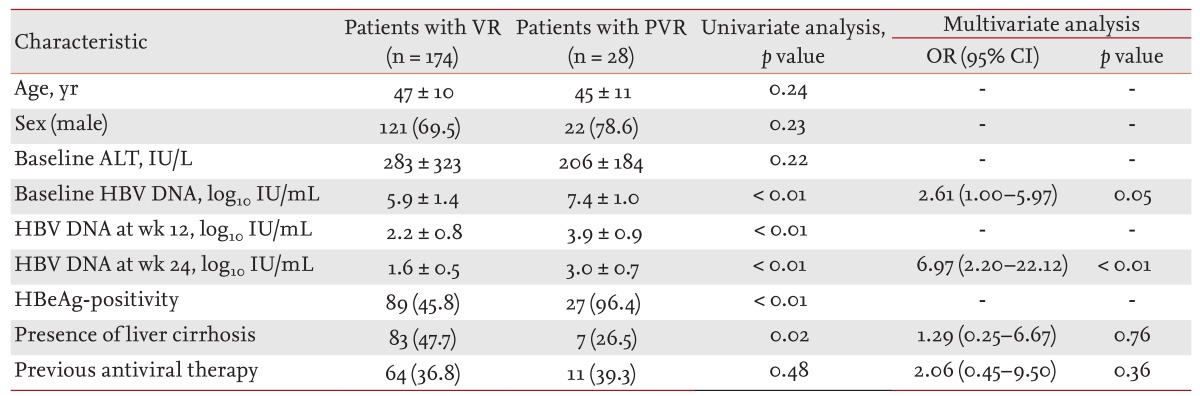
Long Term Virological Outcome In Chronic Hepatitis B Patients With A Partial Virological Response To Entecavir
View Of A Genotype Specific Baseline Score Predicts Post Treatment Response To Peginterferon Alfa 2a In Hepatitis B E Antigen Negative Chronic Hepatitis B Annals Of Gastroenterology

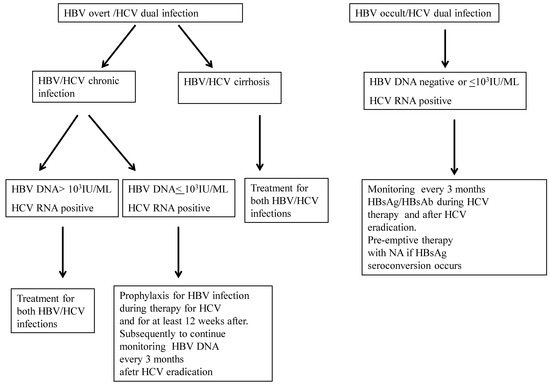
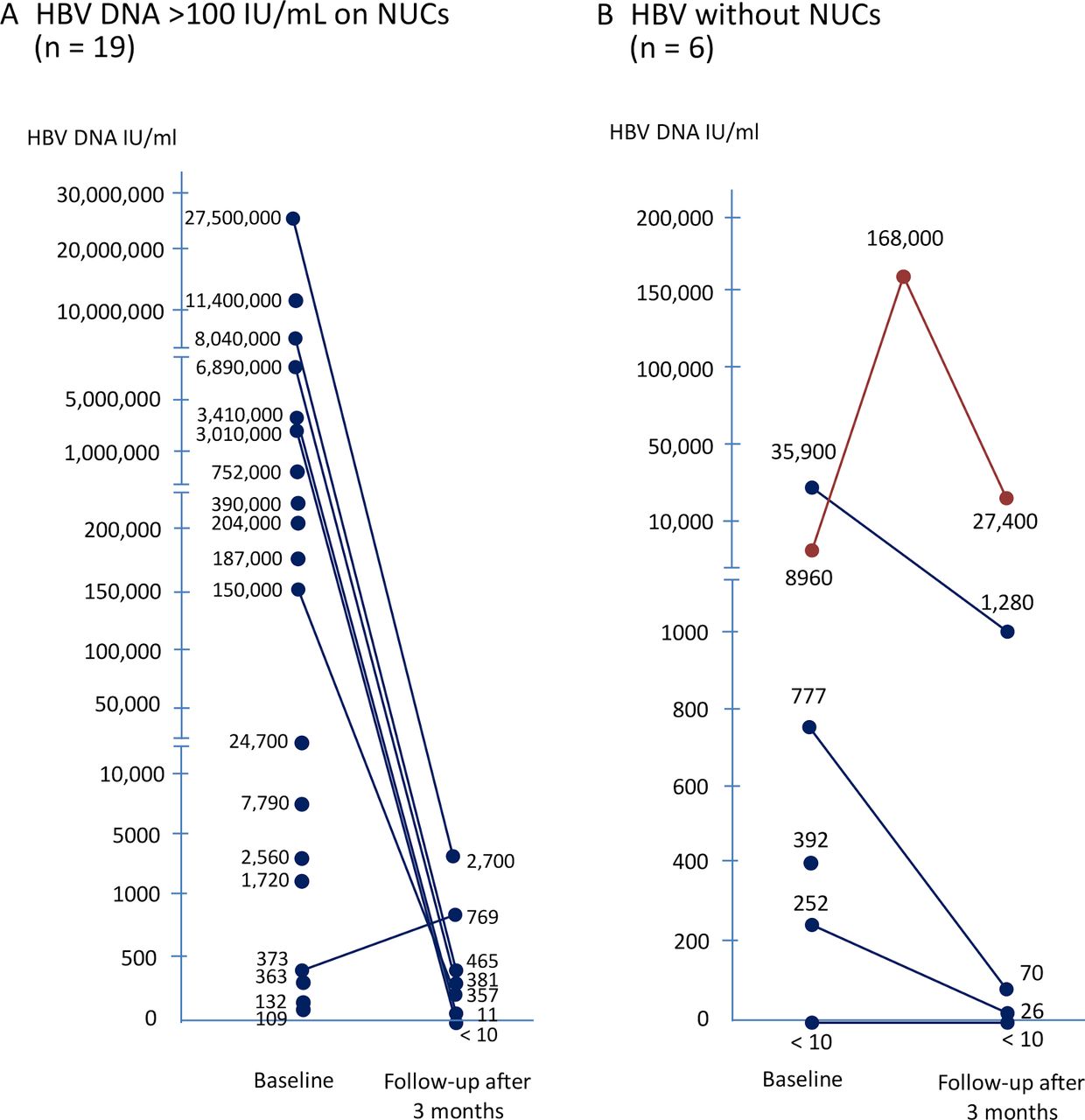
Association Between Negative Results From Tests For Hbv Dna And Rna And Durability Of Response After Discontinuation Of Nucles T Ide Analogue Therapy Sciencedirect
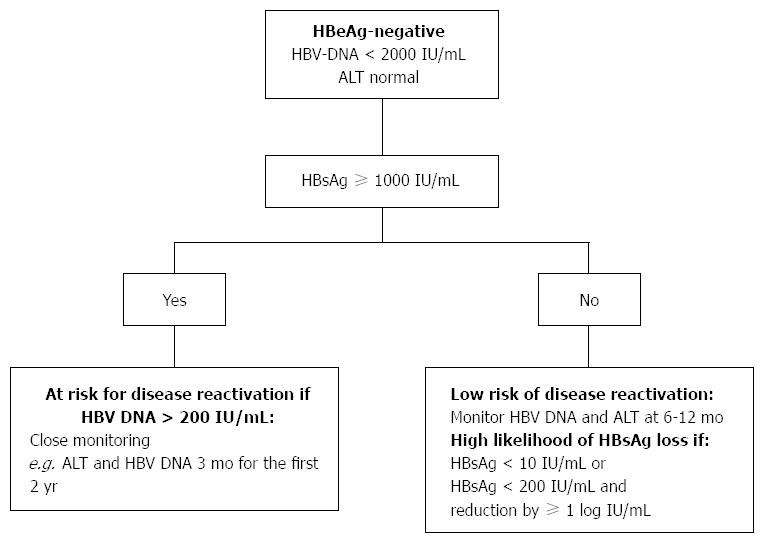
Practical Approach In Hepatitis B E Antigen Negative Individuals To Identify Treatment Candidates

Association Between Negative Results From Tests For Hbv Dna And Rna And Durability Of Response After Discontinuation Of Nucles T Ide Analogue Therapy Sciencedirect
Most HBV-DNA assays used in clinical practice utilize real-time polymerase chain reaction technology with a sensitivity of 5-10 IU/mL and a dynamic range up to 7 log10 IU/mL.
Hbv dna iuml. So 191.7 x 10 (5) = 19,170,000 copies = 3.5 million IU/mL. I had a viral load of Hepatitis C of 0,000 IU/ml for 25 years and only got ill when I was given paracetamol to take daily. HBV DNA is greater than ,000;.
10 lU/mL - 1.0 x 10 9 IU/mL Performance with HBV DNA-negative samples 100.0% "Target Not Detected" (with a two-sided 95% confidence interval of 99.4% - 100%). For detection and quantification of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA in serum or plasma of patients with confirmed chronic HBV infection to monitor disease progression and response to anti-HBV therapy. 95% CI, 1.17-11.) compared with less than.
Xét nghiệm HBV DNA được theo dõi sau mỗi 3-6 tháng cùng với các xét nghiệm khác (AST, ALT, Creatinine máu, HBeAg, Anti-HBe) để đánh giá đáp ứng. 1 IU is equivalent to about 5 HBV DNA copies depending on the assay. Determine the number of international units (IU) of hepatitis B virus DNA per milliliter of serum or plasma in known HBV-positive patients.
A ”Detected” result with the comment, “HBV DNA level is >170,000,000 IU/mL (>8.23 log IU/mL). This is why a confirmed diagnosis of IC requires quarterly ALT and HBV DNA measurements for at least 1 year, while a single-point detection of combined HBsAg <1000 IU/ml and HBV DNA <00 IU/ml has a robust predictive value for the diagnosis of IC. The test is most often used to monitor the efficacy of antiviral therapy in individuals with chronic HBV infection.
The Mean ± SD serum ALT and HBV DNA level was 22.8 ± 8.6 IU/L and 360 ± 4 IU/mL, respectively. 16.4 IU/mL Quantitative Range:. Some patients with CHB have widely fluctuating HBV-DNA levels that may vary from undetectable to >2,000,000 IU/mL.
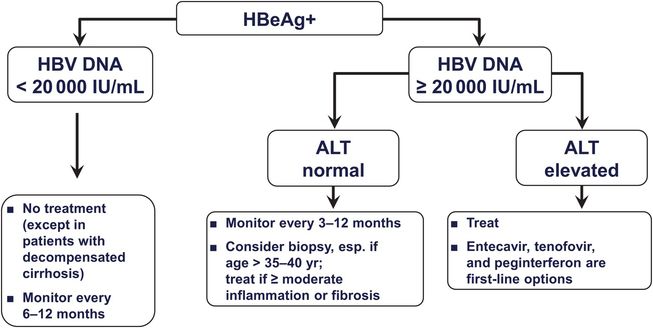
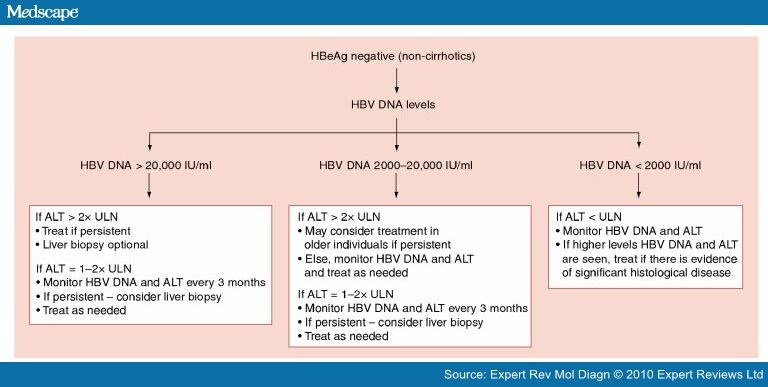
In addition, patients with very low HBsAg (< 100 IU/mL) in combination with an HBV DNA < 00 IU/mL have a high probability of spontaneous HBsAg clearance. ≥4 log 10 IU/ml vs. In general, patients with active HBV (HBV DNA ≥ 2,000 IU/mL if HBeAg-negative and HBV DNA ≥ ,000 IU/mL if HBeAg-positive, and high ALT or evidence of advanced fibrosis) should be considered for HBV antiviral treatment.
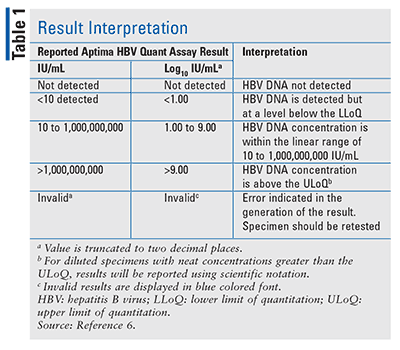
ASR Analyte Specific Reagent (Analytical and performance characteristics are not established) GPR General Purpose Reagent IVD In Vitro Diagnostics (Rx Only) RUO Research Use Only. Limitations Assay range is 10 IU/mL to 1,000,000,000 IU/mL. A result of "<10 IU/mL (<1.00 log IU/mL)" indicates that HBV DNA is detected, but the HBV DNA level present cannot be quantified accurately below this lower limit of quantification of this assay.
Liver biochemistries were per-formed in commercially available autoanalyzers. This test is intended for use as an aid in the management of patients with chronic HBV infection undergoing anti-viral therapy. HBV DNA检测报告中IU/ml与拷贝/ml间的换算 分类: 肝病检测与检查 | 标签: 乙肝病毒DNA 国际单位 拷贝 换算 17:51 阅读 (7902) 评论 (0).
A group of patients <30 y of age (circles) had high viral loads and ALTs from 30 to 50 IU/L, representing ‘immune tolerance’. A bi-opsy is recommended before initiating antiviral therapy1,2 (Fig. Family history of cirrhosis;.
The reportable range is – 170,000,000 IU/mL. When clinically indicated, follow-up testing with this assay is recommended in 1 to 2 months. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), This service is performed pursuant to an agreement with Roche Molecular Systems, Inc.
Adult over 40 years old with an HBV DNA greater than 1 million IU/mL;. This test measures the actual amount of hepatitis B in a blood sample, which helps determine whether HBV is reproducing in the liver. HBV DNA IU/mL (Log 10) HBVQNI:.
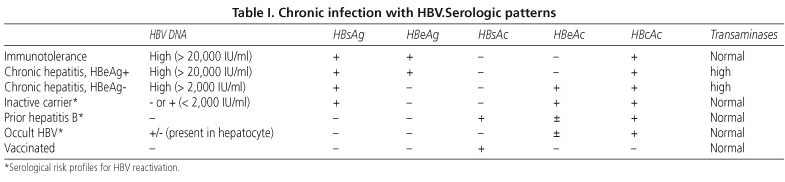
Persons with chronic HBV infection can either be inactive carriers or develop chronic hepatitis. Answer For HBV viral load conversion, 1 IU/ml = 5.6 copies/ml. The limit of detection is 12.5 IU/mL.
The test can be used to measure HBV DNA levels at baseline and during treatment to aid in. An interpretation of "Not Detected" does not rule out the presence of inhibitors in the patient specimen or HBV DNA concentration below the level of detection of the test. Hepatitis B Virus DNA, Quantitative, Real-Time PCR - Chronic carriers will persist in producing detectable HBV.
– 170,000,000 IU/mL (1.3 - 9.2 Log IU/mL) 1 IU/mL of HBV DNA is approximately 5. copies/mL A negative result (“Not Detected”) does not rule out the presence of HBV below the limit of detection of the assay or the presence of inhibitory substances. So i have 47,250 copies/mL?. The 48-week cumulative rate of HBV DNA >00 IU/mL was 58.1%.
The answer above provides general health information that. Patients between 18 and 65 years of age with hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) positivity for more than 6 months, HBV DNA levels >,000 IU/ml for hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg)–positive patients or >00 IU/ml for HBeAg-negative patients, and consent for liver biopsy before receiving antiviral therapy. Only treat normal ALT if.
This test quantitates HBV DNA in serum or plasma with reflex to HBV genotype if ≥500 IU/mL is detected. In a person with detectable HBeAg, an HBV viral load greater than ,000 international units per milliliter (IU/mL) of blood indicates that the virus is active and has the greatest potential to. 1.0E+01 – 1.0E+09 IU/mL (1.0 - 9.0 log IU/mL).
We note at the outset of this review that HBV DNA thresholds may be reported as copies/ml or IU/ml. Xét nghiệm HBV DNA là một trong những xét nghiệm rất quan trọng và cần thiết.Đối với bệnh nhân bị nhiễm virus viêm gan B thì việc kiểm tra định tính, định lượng 5 hạng mục viêm gan B và đếm số virus viêm gan B là rất cần thiết, tuy nhiên, không phải người bệnh nào cũng có thể hiểu được hết ý nghĩa của. Other factors to consider.
Below the threshold, the viral load is considered “undetectable” – something everyone with chronic hepatitis B wants to hear. My question is what does the 4.0 stand for?. Hepatitis B PCR Interpretation Interpretation.
Cobas ® HBV is an in vitro nucleic acid amplification test for the quantitation of hepatitis B virus DNA in human EDTA plasma or serum of HBV-infected individuals. - HBV-DNA ≥ 10 5 copies/ml (.000 IU/ml) nếu HBeAg (+) hoặc HBV- DNA ≥ 10 4 copies/ml (2.000 IU/ml) nếu HBeAg (-). HBV DNA test is the best way to approach this group.
Patients with chronic liver disease of unknown origin most commonly have HBV that is detected by viral DNA testing. HBV DNA not detected. Additionally, among patients with HBV DNA higher than 2,000, liver cancer risk increased among those with HBsAg levels higher than 100 IU/mL (OR = 3.72;.
Patients with HBV DNA > 000 IU/mL and ALT >2xULN (upper limit of normal), HBV DNA >00 IU/mL and liver stiffness >9 or >12 kPa in case of normal or ≤5xULN, HBV DNA >00 IU/mL and a family history of cirrhosis and/or HCC as well as HBeAg-positive patients with HBV DNA > 000 IU/mL and over 30 years old can begin treatment whatever the liver histology. But, the general IU conversion factor is 1.74 copies/IU, or 71,000 IU. Carefully review criteria before initiating antiviral treatment for HBV.
And ≥7 log 10 IU/ml). HR 2.278, 95%. The quantitative range of this assay is 1.00-9.00 log IU/mL (10-1,000,000,000 IU/mL).
Inactive carriers refer to HBeAg-negative individuals who have normal serum ALT levels and low (<. Care should be taken when interpreting any single viral load determination. If Hepatitis B Virus DNA, Quantitative, Real-Time PCR is ≥600 IU/mL, then Hepatitis B Virus Drug Resistance, Genotype, and BCP/Precore Mutations will be performed at an additional charge (CPT code(s):.
Prophylaxis against HBV reactivation. HBeAg-Negative Patients with PNALT and HBV DNA 2,000 IU/mL. Results exceeding 170,000,000 IU/mL will not be diluted, and will be reported as greater than 170,000,000 IU/mL.
The disease continues to progress in a substantial proportion of patients who achieve standard milestones, such as HBeAg seroconversion, HBsAg clearance, HBV DNA levels less than 105 copies/mL ( 000 IU/mL) or even 104 copies/mL (00 IU/mL), and ALT levels between 0.5 and 2 times the upper limit of normal. The sensitivity of HBV DNA tests may vary with each lab so it’s a good idea to use the same lab for your test. <4 log 10 IU/ml;.
The conversion factor is 1 IU/ml ≈5.3 copies/ml, but generally a threshold of 00 IU/ml is taken to correspond to 10,000 copies/ml (or 4 log10 copies/ml). The optimal management of HBeAg-nega-tive patients with PNALT and HBV DNA 2,000 IU/mL has been the subject of a recent systematic review.9 HBeAg-FIGURE 1. A positive HBV-DNA level (greater than 115 copies of the virus per mL > IU/mL) indicates that the virus is multiplying in the individual’s body and the person is contagious.
Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction, Quantitative. Reference Range See individual components Guidelines. ALT and HBV DNA viral loads are shown for the entire cohort in Figure 4.
Some Hepatitis B loads are so low as be judged harmless infection and illness wise as they are below 0 to 500, more traces of a past infection than actually having enough Hepatitis B to ever get ill. An "Undetected" result indicates that hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA was not detected in the serum specimen. The HBV DNA level was ≥ 0 IU/mL in 86 (41.3%) patients.
Main inclusion criteria were as follows:. Quantitative measurement of HBV viral DNA may be used to monitor progression of disease. HBV DNA Not Detected <1.00E+1 IU/mL HBV DNA detected below the linear range of the assay.
HBV DNA levels between 2,000 and ,000 IU/mL. Is it the same as 9,450 IU/ML?. The World Health Organization created a standard for measuring HBV DNA, it established the international unit (IU) or copies per milliliter (mL), written as IU/mL or copies/mL.
Value Flag Reference Range HEPATITIS B DNA QNT PCT 4.0 H < 1.6 log IU **** Viral load result for HBV DNA is 9,450 IU/ML*** 1 IU/ML is 5 copies/mL. Were converted to IU/mL, considering that 0.15 ng/mL of HBsAg is equivalent to 350 IU/mL." This seems to vary significantly from the usual conversion rules of:. These HBV DNA and qHBsAg cutoffs have also been associated with a lower risk for HCC and liver disease progression.
If your lab doesn’t use that measurement, it should be able to convert your results into copies/mL or IU/mL. A result of "<10 IU/mL (<1.00 log IU/mL)" indicates that HBV DNA is detected, but the HBV DNA level present cannot be quantified accurately below this lower limit of quantification of this assay. Hbv dna“< iu/ml”与“tnd”一样吗? hbv dna“< iu/ml”是指hbv dna仍能检测到,只是水平太低,低于 iu/ml这个最低检测值,无法准确读出数值。而“tnd”是在这个标本中根本没有检测到hbv dna。因此,可以认为hbv dna“tnd”这个结果比“< iu/ml”更好。.
There was no case with persistently normal ALT and HBV DNA levels higher than ,000 IU/mL. The majority of participants had an ALT <50 IU/L and HBV DNA < 000 IU/ml (59/100). But not all labs in the United States use this standard.
<7 log 10 IU/ml;. If you are speaking about HIV viral load, HIV viral load results are not usually expressed in IU. End-of-treatment serum HBV RNA and off-treatment serial HBV RNA were both independently associated with HBV DNA >00 IU/mL (HR 2.959, 95% CI 1.776 to 4.926, p<0.001;.
1 ng/ml = 0.2 iu/ml or. Family history of hepatocellular carcinoma;. Older age (over 40 years old) Extrahepatic manifestations of HBV;.
The HBeAg status was set as positive or negative, and the baseline HBV DNA load was divided into four grades (<2 log 10 IU/ml;. For these patients, HBeAg. Table 1 Baseline characteristics of HBV carriers according to the development of abnormal ALT levels or HBV reactivation within one year.
In HBV DNA viral load estimation, what is the equivalent of IU/ml = log10 IU/ml or log10 copies/ml?. ≥2 log 10 IU/ml vs. Results 114 entecavir-treated patients (median age 58.4 years, median serum HBsAg 54.4 IU/mL) with median treatment duration of 6.7 years were recruited.
The ULNwas40IU/LforbothALTandAST.HepatitisA,B, D, C virus and HIV 1,2 serological markers (anti-HAV,. Theo dõi trong và sau điều trị:.
Efficacy And Safety Of Tenofovir Disoproxil Furmarate For Patients With Lamivudine Resistant Hepatitis B Virus Infection Kwon Journal Of Gastroenterology And Hepatology Research

Changing Serum Levels Of Quantitative Hepatitis B Surface Antigen And Hepatitis B Virus Dna In Hepatitis B Virus Surface Antigen Carriers A Follow Up Study Of An Elderly Cohort Sciencedirect
Www Cancerwa Asn Au Resources 18 05 06 Hbv Dr Mitchell Pdf

Association Of Hepatitis B E Antigen And Dna Viral Load With Severity Of Liver Dysfunction And In Hospital Outcomes In Hepatitis B Related Liver Cirrhosis Hou Ame Medical Journal

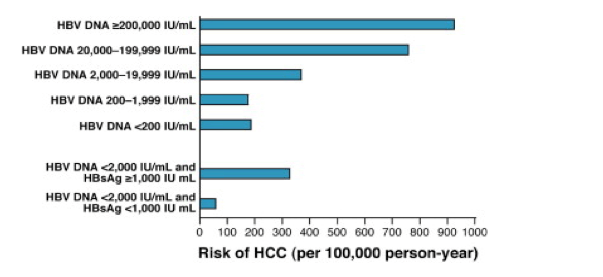
High Levels Of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Increase Risk Of Hepatocellular Carcinoma In Patients With Low Hbv Load Gastroenterology

A Real Time Quantitative Assay For Hepatitis B Dna Virus Hbv Developed To Detect All Hbv Genotypes
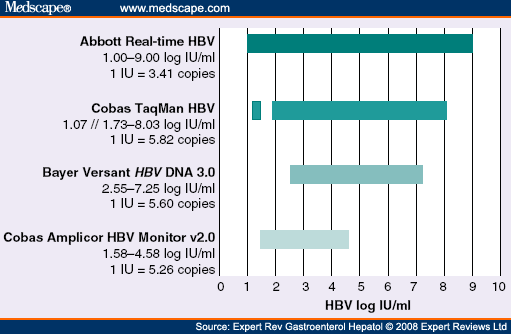
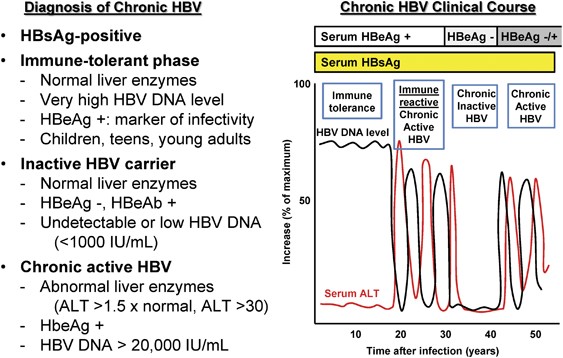
Diagnosis Of Hepatitis B Virus Infection
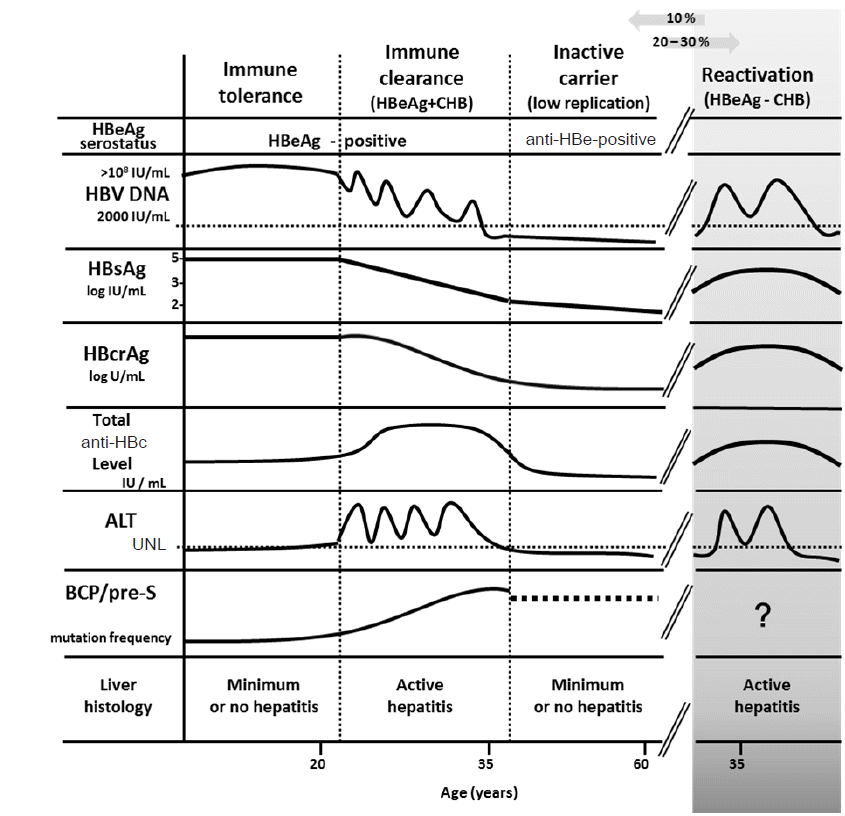
Cmh Clinical And Molecular Hepatology Clin Mol Hepatol 2287 2728 2287 285x The Korean Association For The Study Of The Liver 10 3350 Cmh 16 0069 Cmh 16 0069 Review New Perspectives Of Biomarkers For The Management Of Chronic Hepatitis B
View Of A Genotype Specific Baseline Score Predicts Post Treatment Response To Peginterferon Alfa 2a In Hepatitis B E Antigen Negative Chronic Hepatitis B Annals Of Gastroenterology
Www Cghjournal Org Article S1542 3565 16 1 Pdf

Fig 36 Coupled Forest Plot Of The Performance Of Hbv Dna 5 Log10 Iu Ml During Pregnancy To Predict Mtct Of Hbv By Type Of Hbv Dna Assay Prevention Of Mother To Child Transmission
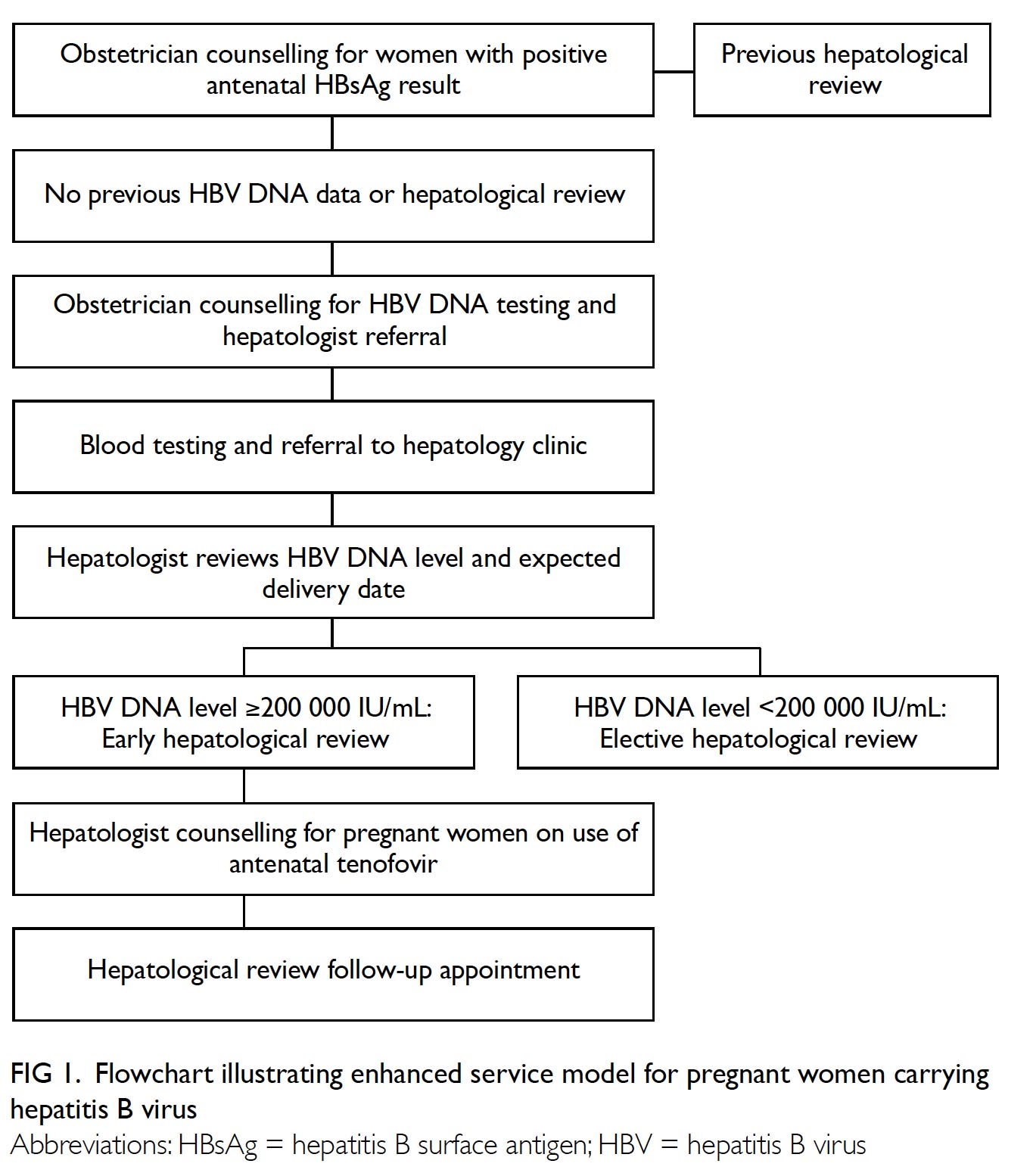
Acceptance Of Antiviral Treatment And Enhanced Service Model For Pregnant Patients Carrying Hepatitis B Hkmj

Chronic Hepatitis B In Pregnant Women Is Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Quantification Useful For Viral Load Prediction International Journal Of Infectious Diseases

Mqkae 3nofvuym

Dominance Of Hepatitis C Virus Hcv Is Associated With Lower Quantitative Hepatitis B Surface Antigen And Higher Serum Interferon G Induced Protein 10 Levels In Hbv Hcv Coinfected Patients Clinical Microbiology And Infection

Treatment Of Chronic Hepatitis B An Update And Prospect For Cure Intechopen
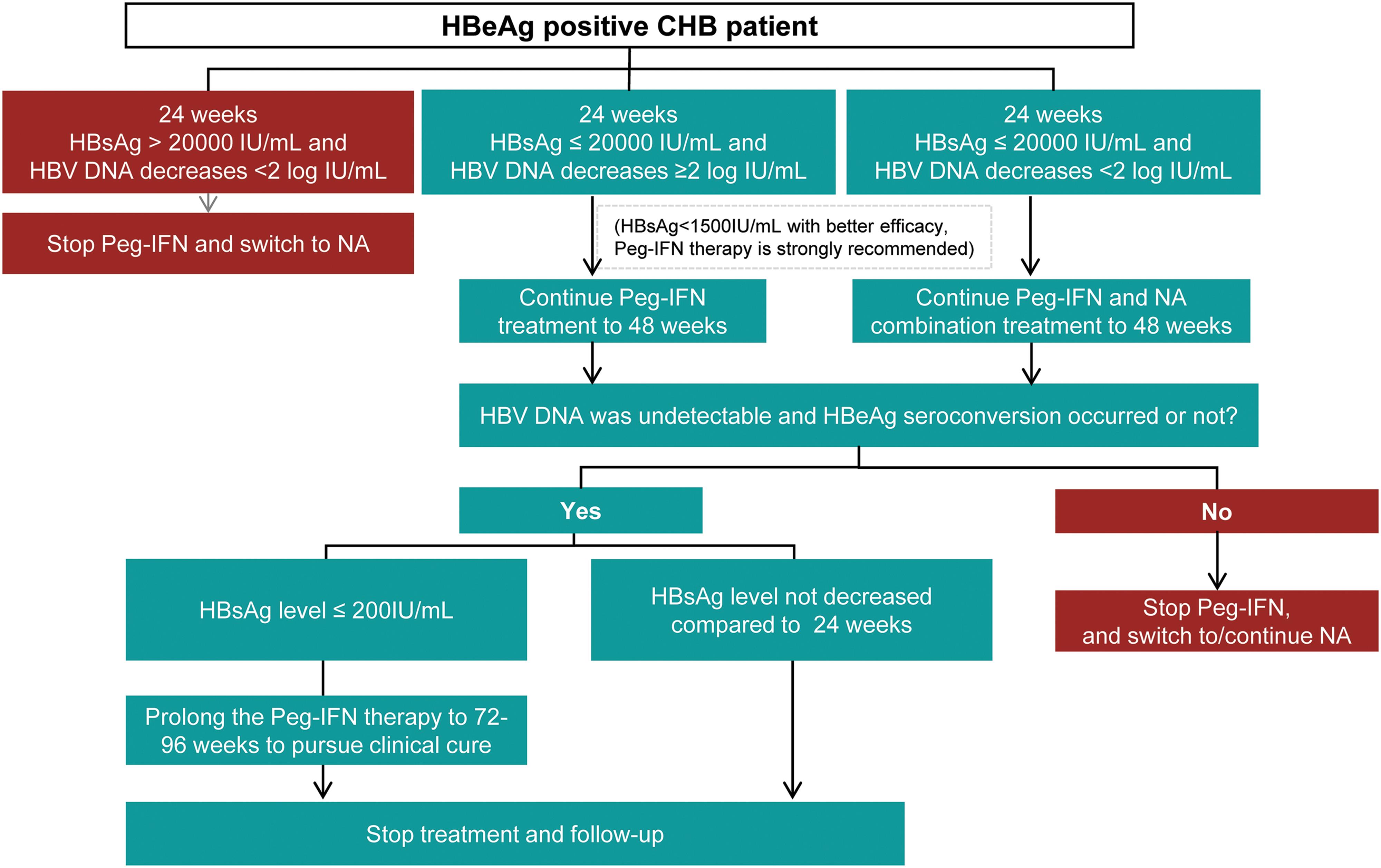
Consensus On Pegylated Interferon Alpha In Treatment Of Chronic Hepatitis B
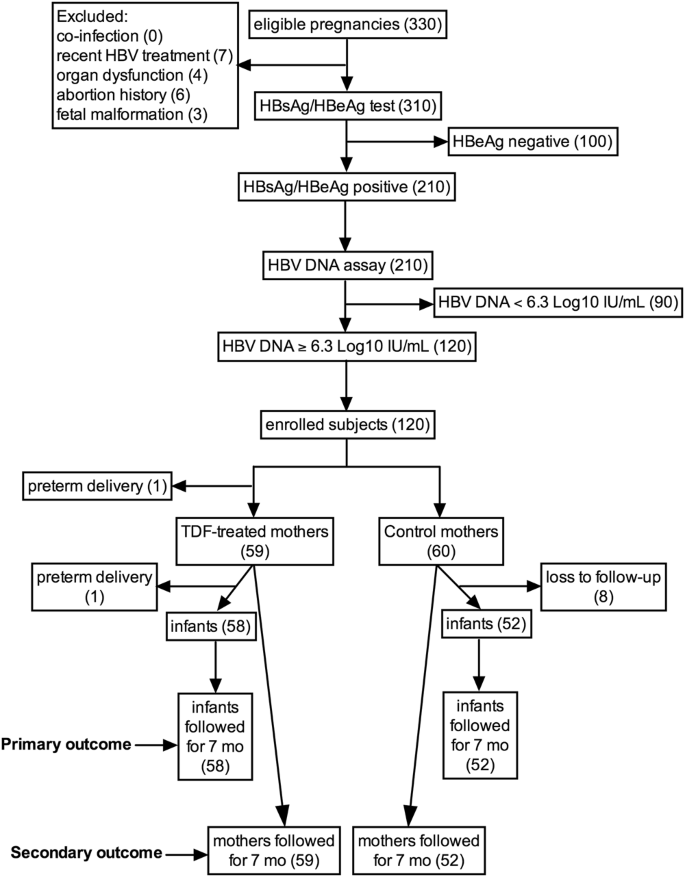
Efficacy Of Tenofovir In Preventing Perinatal Transmission Of Hbv Infection In Pregnant Women With High Viral Loads Scientific Reports
Reactivacion De La Hepatitis B Y Su Impacto Clinico Actual
Q Tbn 3aand9gctnczk Zeoncwquzv2jaw2oul3fzjozccljyt0z9wy9fcfvlsjh Usqp Cau

Hepatitis B Virus Dna Stability In Plasma Samples Under Short Term Storage At 42 C
Serum Hbv Rna Quantification Useful For Monitoring Natural History Of Chronic Hepatitis B Infection Bmc Gastroenterology Full Text

Zacks Small Cap Research Arwr New Hbv Clinical Data Of Arc 5 Presented At Hep Dart Meeting
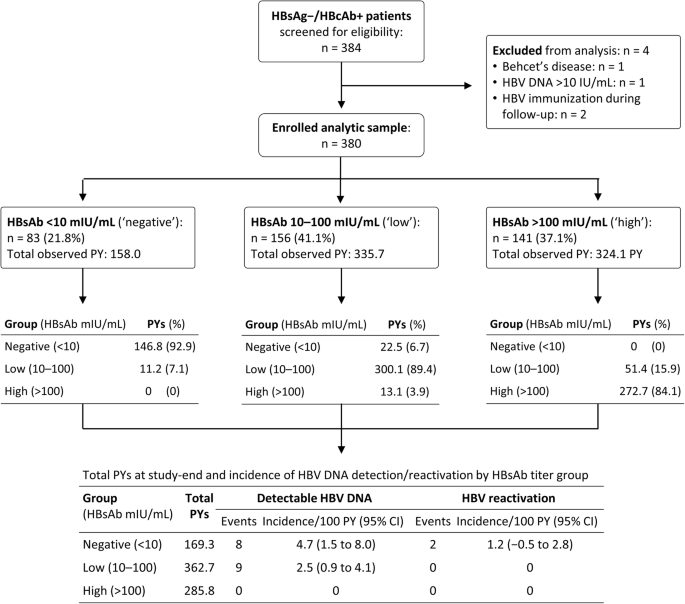
Changes In Hepatitis B Virus Surface Antibody Titer And Risk Of Hepatitis B Reactivation In Hbsag Negative Hbcab Positive Patients Undergoing Biologic Therapy For Rheumatic Diseases A Prospective Cohort Study Arthritis Research Therapy
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqnwp Xvmvowm19jjgu51mzg47ruk0vx S0xbwekonky64drr62 Usqp Cau

Baseline Characteristics Of 251spontaneous Hbeag Seroconverters With Download Table

Management Of Chronic Hepatitis B An Overview Of Practice Guidelines For Primary Care Providers American Board Of Family Medicine

Zacks Small Cap Research Arwr New Hbv Clinical Data Of Arc 5 Presented At Hep Dart Meeting
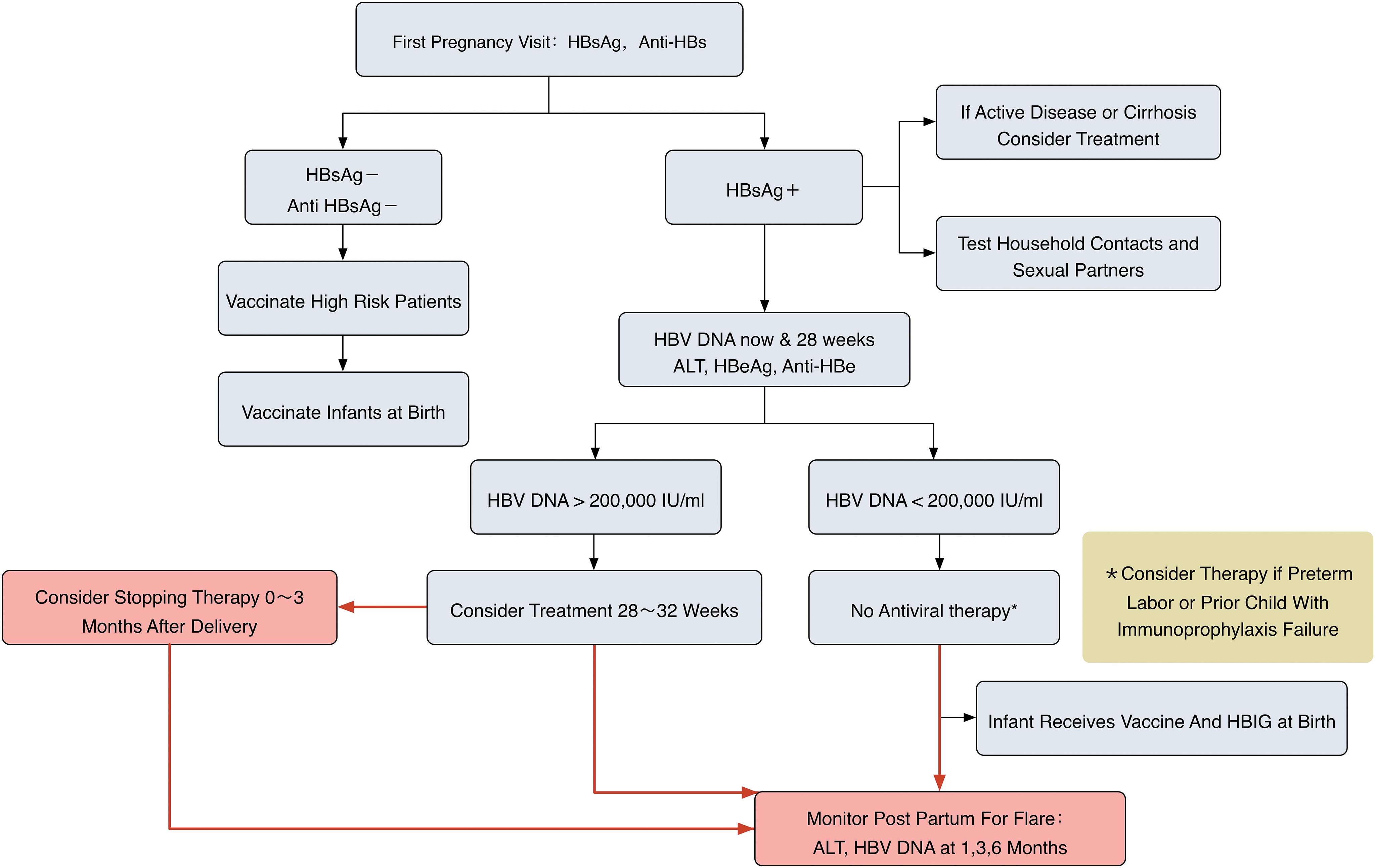
Hepatitis B Management In The Pregnant Patient An Update

Management Of Hepatitis B In Special Populations Abstract Europe Pmc

Article
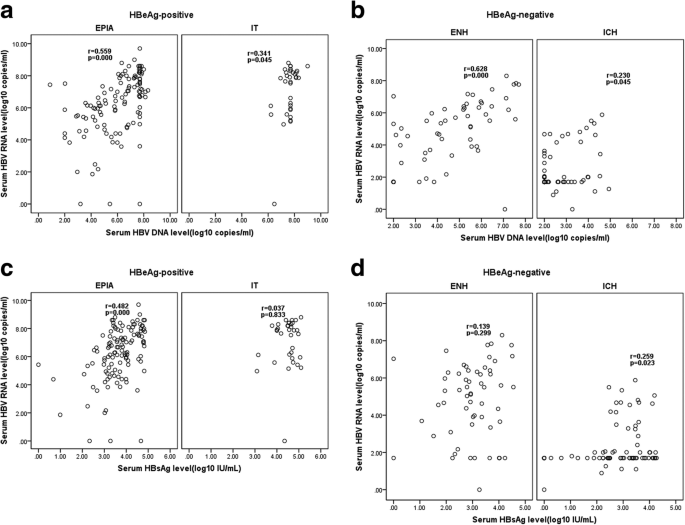
Plos One Prediction Of Clinical Outcomes In Hepatitis B E Antigen Negative Chronic Hepatitis B Patients With Elevated Hepatitis B Virus Dna Levels

Hepatitis Monthly Characterization Of Serum Hbv Rna In Patients With Untreated Hbeag Positive And Negative Chronic Hepatitis B Infection

Full Text Characteristics Of Hbv Infection In 705 Hiv Infected Patients Under La Idr
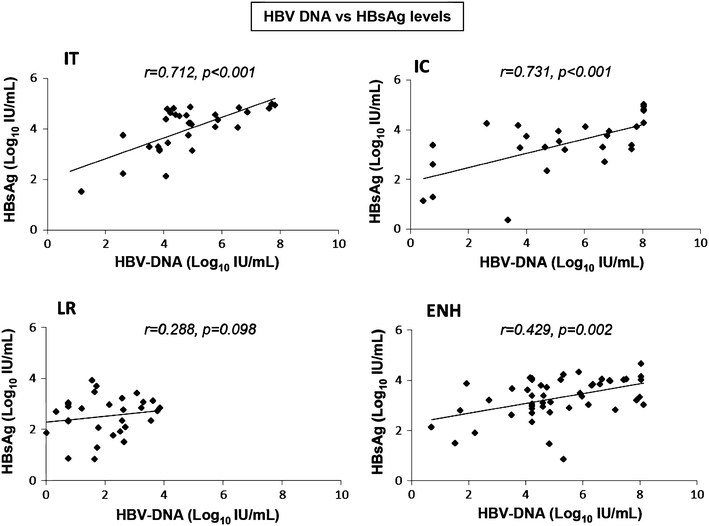
Figure 1 Hbsag Hbeag And Hbv Dna Level Changes And Precore Basal Core Promoter Mutations In The Natural History Of Chronic Hepatitis B In Indonesian Patients Springerlink

Association Of Hepatitis B E Antigen And Dna Viral Load With Severity Of Liver Dysfunction And In Hospital Outcomes In Hepatitis B Related Liver Cirrhosis Hou Ame Medical Journal

Full Text Serum Hepatitis B Core Antibody Levels Predict Hbeag Seroconversion In Idr

Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection The Lancet
Hbv Treatment And Management Hepatic Health

Hbv Dna Level Of Each Rflp Elisa Hbv Genotyped Group Log Iu Ml Download Table
Viruses Free Full Text Hepatitis B Virus Hbv Reactivation Following Pharmacological Eradication Of Hepatitis C Virus Hcv Html
International Medical Press Browse Articles
Q Tbn 3aand9gct3oprcobs1fv0fftzrcflzxn1 Aclaov5irr4d3kennel8wc M Usqp Cau

Comprehensive 18 sld Guidance For Chronic Hepatitis B Gutsandgrowth
Www Cghjournal Org Article S1542 3565 19 6 Pdf

Rebound Of Hbv Dna After Cessation Of Nucleos Tide Analogues In Chronic Hepatitis B Patients With Undetectable Covalently Closed Circular Dna Jhep Reports
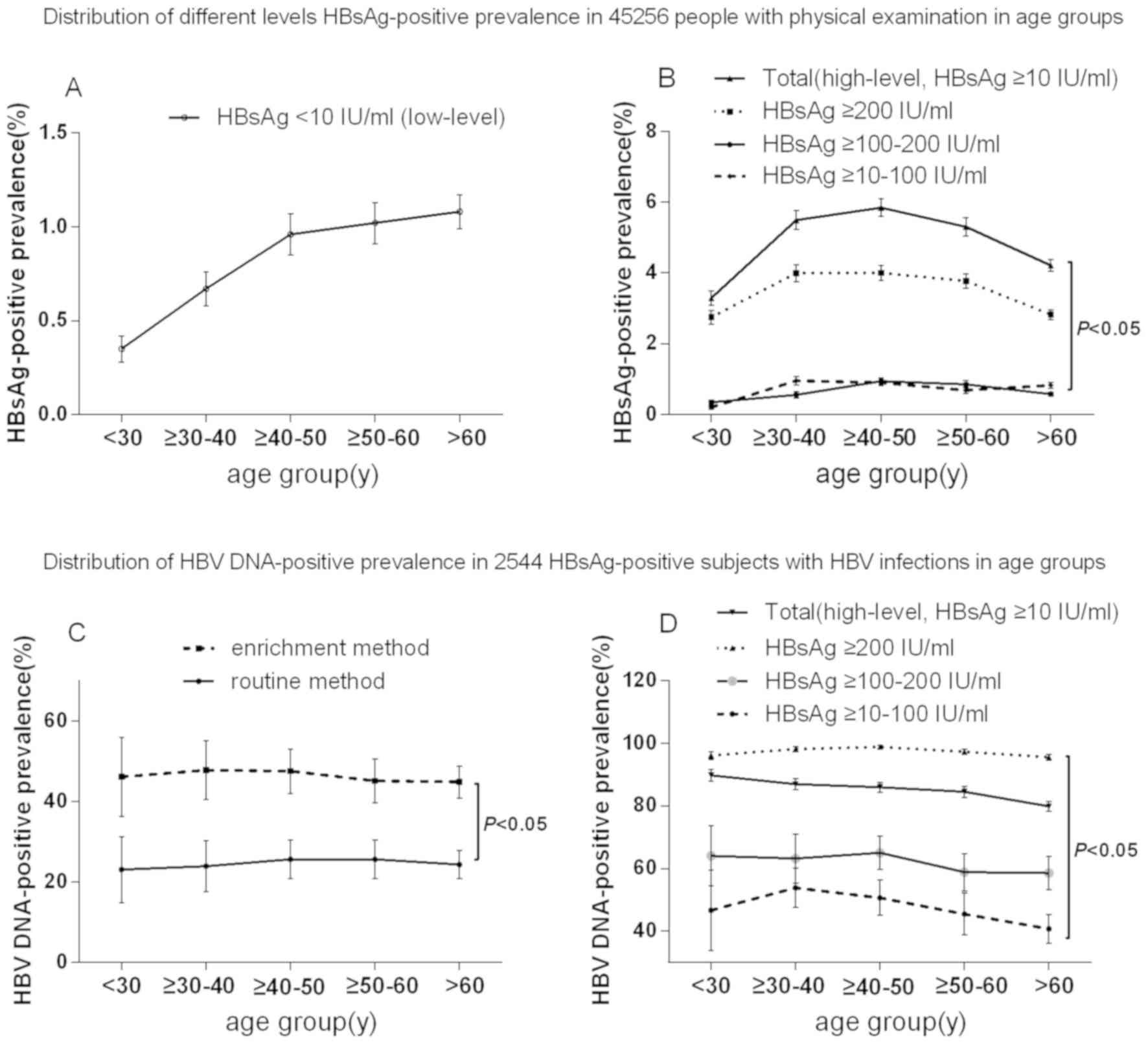
Clinical Characteristics And Association Analysis Of Persistent Low Level Hbsag Expression In A Physical Examination Population With Hbv Infection

Diagnostic Value Of Detection Of Pregenomic Rna In Sera Of Hepatitis B Virus Infected Patients With Different Clinical Outcomes Journal Of Clinical Microbiology
Chronic Hepatitis Oncohema Key

Fig 6 Coupled Forest Plot Of The Performance Of Hbeag To Identify Maternal Hbv Dna 5 Log10 Iu Ml By Who Region Prevention Of Mother To Child Transmission Of Hepatitis B Virus Guidelines On

Inasl Position Statements On Prevention Diagnosis And Management Of Hepatitis B Virus Infection In India The Andaman Statements Journal Of Clinical And Experimental Hepatology
Tim 3 Expression On T Cells Is Correlated With Liver Inflammation Fibrosis And Virological Characteristics In Treatment Naive Chronic Hepatitis B Patients A Cross Sectional Study Gu Annals Of Blood
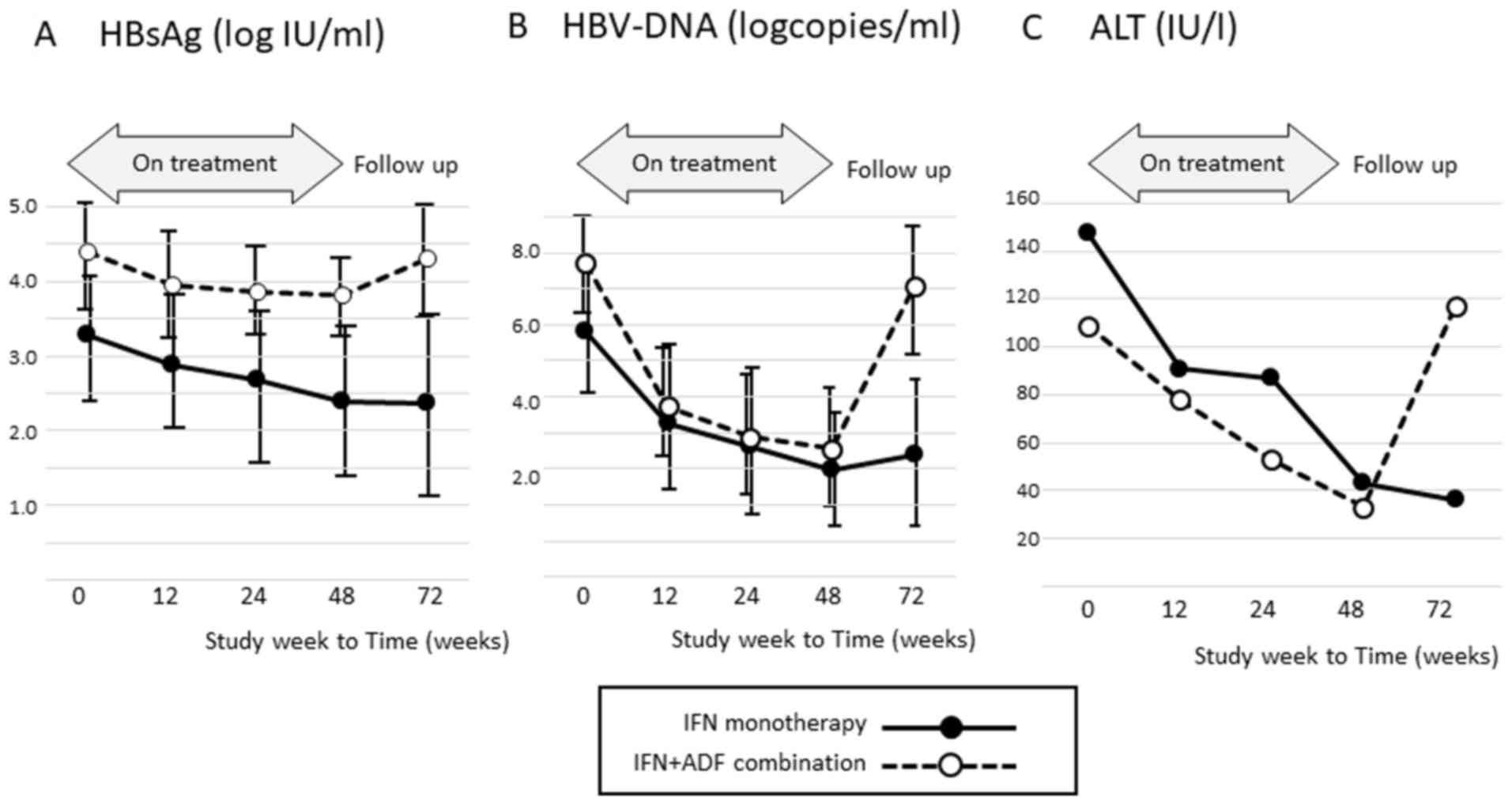
Factors Associated With The Decrease In Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Titers Following Interferon Therapy In Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Is Interferon And Adefovir Combination Therapy Effective
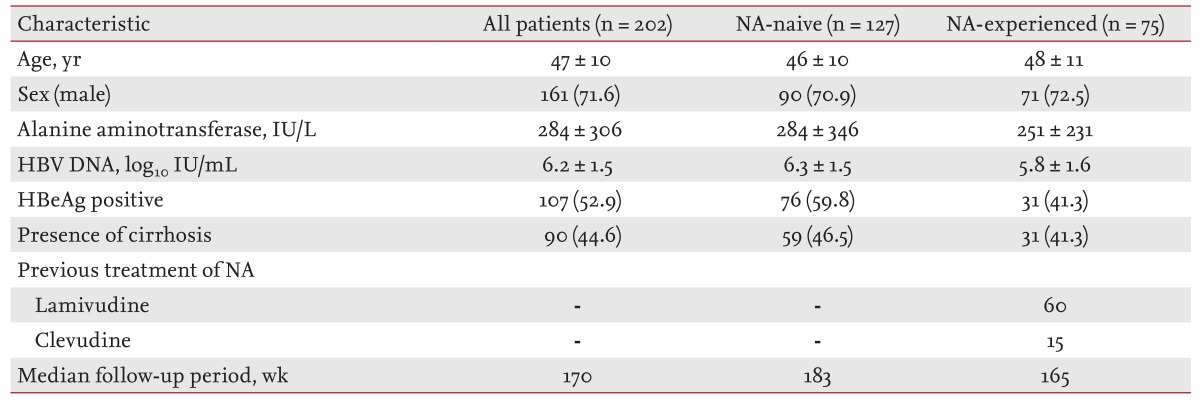
Long Term Virological Outcome In Chronic Hepatitis B Patients With A Partial Virological Response To Entecavir

Evaluation Of The Cobas Ampliprep Total Nucleic Acid Isolation Cobas Taqman Hepatitis B Virus Hbv Quantitative Test And Comparison To The Versant Hbv Dna 3 0 Assay Journal Of Clinical Microbiology
Molecular Methods In The Diagnosis And Management Of Chronic Hepatitis B

Recommendations For Screening Monitoring And Referral Of Pediatric Chronic Hepatitis B American Academy Of Pediatrics
Replication Inhibition Of Hepatitis B Virus And Hepatitis C Virus In Co Infected Patients In Chinese Population

Poster Session 3 Hepatitis B Epidemiology And Natural History History 15 Hepatology Wiley Online Library
Www Medicine Uci Edu Gisymposium Pdf Pan Pdf
Risk Of Hbv Reactivation In Patients With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treated Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma Journal For Immunotherapy Of Cancer

Evaluation Of Hepatitis B Virus In Clinical Trials Of Baricitinib In Rheumatoid Arthritis Rmd Open

Correlation Between Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Titers And Hbv Dna Levels Alghamdi A Aref N El Hazmi M Al Hamoudi W Alswat K Helmy A Sanai Fm Abdo Saudi J Gastroenterol

Serum Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Levels Correlate With High Serum Hbv Dna Levels In Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B A Cross Sectional Study Gupta E Kumar A Choudhary A Kumar M Sarin S K
Identifying Hepatitis B Carriers At Low Risk For Hepatocellular Carcinoma Editorial

Hepatitis Monthly Characterization Of Serum Hbv Rna In Patients With Untreated Hbeag Positive And Negative Chronic Hepatitis B Infection

Roc Curve Analysis Using Hbsag 900 Iu Ml For Prediction Of Hbv Download Table
Http Regist2 Virology Education Com 17 15euhivhep 13 Battisti Pdf
Hepatitis B And C In Pregnancy A Review And Recommendations For Care Journal Of Perinatology

Low Hepatitis B Surface Antigen And Hbv Dna Levels Predict Response To The Addition Of Pegylated Interferon To Entecavir In Hepatitis B E Antigen Positive Chronic Hepatitis B Liem 19

Use Of Hepatitis B Virus Core Related Antigen To Evaluate Natural History Of Chronic Hepatitis B Chan Journal Of Gastroenterology And Hepatology Wiley Online Library

Characteristics Of Hepatitis B Core Antibody Level In The Natural History Of Chronic Hepatitis B Jian Wang Discovery Medicine

Safety And Efficacy Of Stopping Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate In Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Following At Least 8 Years Of Therapy A Prespecified Follow Up Analysis Of Two Randomised Trials The Lancet

Add On Pegylated Interferon Augments Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Clearance Vs Continuous Nucleos T Ide Analog Monotherapy In Chinese Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B And Hepatitis B Surface Antigen 1500 Iu Ml An Observational Study
Plos One Total Hepatitis B Core Antigen Antibody A Quantitative Non Invasive Marker Of Hepatitis B Virus Induced Liver Disease

Core Concepts Hepatitis B Co Infection Co Occurring Conditions National Hiv Curriculum
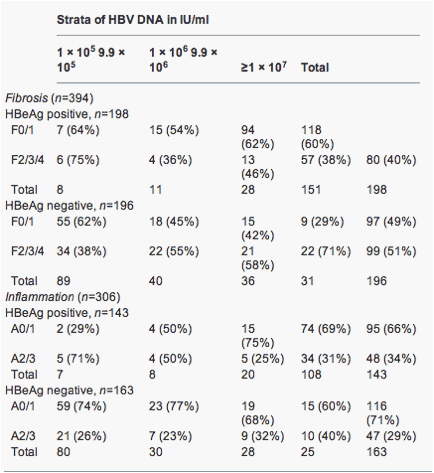
Hbv Viral Load Fibrosis Alt Inflammation Hbeag Hbeag Increasing Hepatitis B Viral Load Is Associated With Risk Of Significant Liver Fibrosis In Hbeag Negative But Not Hbeag Positive Chronic Hepatitis B
Aptima Hbv Quant Assay

Mean Reduction In Serum Hepatitis B Virus Hbv Dna Log10 Iu Ml From Download Scientific Diagram

Serum Vitamin D Levels In Treatment Naive Chronic Hepatitis B Patients In Journal Of Translational Internal Medicine Volume 5 Issue 4 17

Performance Comparison Of The Artus Hbv Qs Rgq And The Cap Ctm Hbv V2 0 Assays Regarding Hepatitis B Virus Dna Quantification
Www Aphc Info Wp Content Uploads 14 10 Maurizia Brunetto Pdf
Http Www Gastrojournal Org Article S0016 5085 10 8 Pdf

Serum Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Levels Correlate With High Serum Hbv Dna Levels In Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B A Cross Sectional Study Gupta E Kumar A Choudhary A Kumar M Sarin S K
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrdabd47qhxgwslbvoggjkmkvnkojz1y9nauril5xz93zntykr3 Usqp Cau
Short Term Spontaneous Fluctuations Of Hbv Dna Levels In A Senegalese Population With Chronic Hepatitis B Bmc Infectious Diseases Full Text
Progression And Status Of Antiviral Monitoring In Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B From Hbsag To Hbv Rna
Prevalence And Characterization Of Occult Hepatitis B Infection Among Blood Donors In Central Saudi Arabia Alshayea Saudi Medical Journal
Article Introduction Of Routine Hepatitis B Screening For All Patients Receiving Cancer Treatment Full Text January 19 Njm

Factors Associated With Active Hbv Replication Hbv Dna 10 Iu Ml Download Table
The Role Of Hbsag Levels In The Current Management Of Chronic Hbv Infection

Performance Comparison Of The Artus Hbv Qs Rgq And The Cap Ctm Hbv V2 0 Assays Regarding Hepatitis B Virus Dna Quantification

Baseline Characteristics Of 251spontaneous Hbeag Seroconverters With Download Table

Comparison Of Different Hepatitis B Guidelines Sethy Pk Goenka Mk Hep B Annual
Plos One High Endemicity And Low Molecular Diversity Of Hepatitis B Virus Infections In Pregnant Women In A Rural District Of North Cameroon

Hepatitis B Virus Genotypes Precore Mutations And Basal Core Promoter Mutations In Hbv Infected Chinese Patients With Persistently Normal Alanine Aminotransferase And Low Serum Hbv Dna Levels
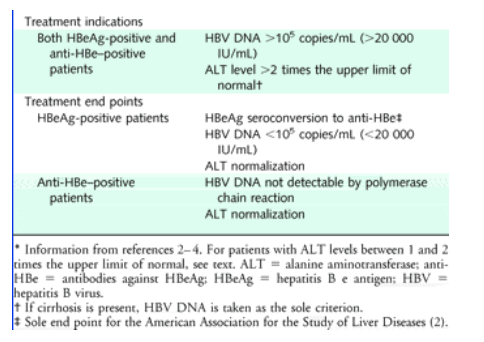
The Natural History And Treatment Of Chronic Hepatitis B A Critical Evaluation Of Standard Treatment Criteria And End Points Hbv Dna Alt

Serum Hepatitis B Virus Dna Rna And Hbsag Which Correlated Better With Intrahepatic Covalently Closed Circular Dna Before And After Nucleos T Ide Analogue Treatment Journal Of Clinical Microbiology



